What is UX?
User Experience (UX) refers to the overall experience a person has when interacting with a product, system, or service. It encompasses a user’s perceptions, emotions, and responses as they engage with a particular product or service, focusing on aspects such as usability, accessibility, and overall satisfaction. UX design involves understanding the users’ needs and behaviors, creating a seamless and intuitive interface, and ensuring that the entire interaction is efficient and enjoyable. Ultimately, the goal is to design experiences that are meaningful, relevant, and valuable to users, leading to enhanced user satisfaction and long-term engagement.
Importance of UX
User experience is crucial because it directly impacts how users perceive and interact with products or services. A positive user experience can lead to enhanced customer satisfaction, brand loyalty, and increased user engagement. On the other hand, a poor user experience can result in user frustration, decreased usage, and negative brand perception.
Principles
User Experience design is guided by a set of fundamental principles that help designers create products and services that meet user needs and deliver exceptional experiences. These principles serve as a framework for designing intuitive, efficient, and user-centered solutions. Let’s explore some key principles that underpin UX design.
1. User-Centered Design: At the core of UX design is the principle of putting users at the center of the design process. This involves understanding user behaviors, needs, and goals through methods such as user research, personas, and user journey mapping. By empathizing with users, designers can create products that resonate with their intended audience.
2. Usability: Usability is a critical principle that focuses on making products easy to use and navigate. This involves designing intuitive user interfaces, clear navigation, and ensuring that users can accomplish tasks efficiently. Usability testing is often employed to identify and address usability issues throughout the design process.
3. Accessibility: The principle of accessibility emphasizes designing products that are inclusive and can be used by individuals with disabilities. This involves considerations such as providing alternative text for images, ensuring keyboard navigation, and adhering to web accessibility standards such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines).
4. Consistency: Consistency in design is essential for creating a cohesive and predictable user experience. This principle involves maintaining uniformity in visual elements, interactions, and terminology throughout the product. Consistent design patterns and standards help users feel oriented and confident in their interactions.
5. Feedback and Iteration: Gathering user feedback and continuously iterating on designs is a foundational principle of UX. This involves incorporating user feedback from usability testing, analytics, and user interviews to refine and improve the user experience. Iterative design allows for ongoing enhancements based on user input, ensuring that the product evolves to meet changing user needs.
6. Visual Hierarchy: Visual hierarchy is a principle that involves organizing content and elements in a way that guides users’ attention and communicates the relative importance of information. This includes considerations such as contrast, sizing, and placement to prioritize key elements and aid users in effectively navigating the interface.
7. Simplicity: The principle of simplicity emphasizes the importance of creating straightforward and uncomplicated user experiences. By minimizing cognitive load and reducing unnecessary complexity, designers can create intuitive and user-friendly interfaces that are easy to understand and use.
8. Emotional Design: Emotional design focuses on evoking positive emotions and creating memorable experiences for users. This principle acknowledges that user experiences are not solely rational but also emotionally driven. Attention to aesthetics, storytelling, and creating a delightful experience contributes to the emotional impact of the user experience.
Processes of UX
UX processes typically involve the following key stages:
1. User Research: Understanding user behavior, needs, and pain points through methods such as interviews, surveys, and observation.
2. Information Architecture: Organizing and structuring information in a logical and user-friendly manner.
3. Interaction Design: Designing how users interact with the product, including the layout of elements and the overall flow of interactions.
4. Prototyping and Testing: Creating interactive prototypes to gather feedback from users and refine the design.
5. Implementation: Collaborating with development teams to ensure the final product reflects the intended user experience.
Tools for UX
There are numerous tools available to aid in the UX design process, including:
1. Design and Prototyping Tools: Software such as Sketch, Adobe XD, and Figma for creating mockups and prototypes.
2. User Research Tools: Platforms like UserTesting and Optimal Workshop for conducting user research and usability testing.
3. Analytics and Tracking Tools: Applications like Google Analytics and Hotjar for tracking user behavior and interactions.
4. Collaboration Tools: Platforms such as InVision and Miro for facilitating collaboration among design and development teams.
Current Trends
Several trends are shaping the future of UX design. Some of these include:
1. Personalization: Tailoring experiences to individual user preferences and behaviors.
2. Voice User Interfaces (VUI): Designing for voice interactions as voice assistants become more prevalent.
3. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Designing immersive experiences for AR and VR environments.
4. Ethical Design: Incorporating ethical considerations, such as privacy and data security, into the design process.
By understanding and incorporating these principles, processes, tools, and trends, designers and organizations can create user experiences that not only meet user needs but also exceed their expectations, leading to user satisfaction and business success.

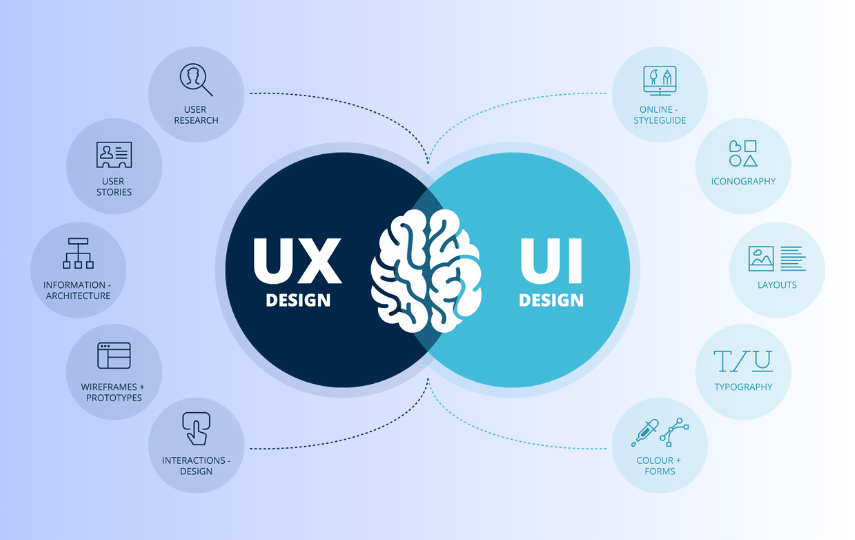
What does poor user experience mean?
Hello,
A poor user experience occurs when a product, service, or system fails to meet user expectations, leading to frustration, confusion, or dissatisfaction. This might be due to slow loading times, difficult navigation, unclear instructions, or other factors that make it hard for users to achieve their goals easily. Poor user experience can result in reduced satisfaction and engagement, impacting the success of the product or service.
Hello Katy Fard,
Please name some tools for understanding user feedback from statistics.
Hello Jinous,
In UX design, there are tools like Google Analytics to see how many people visit a website and what they do there. Hotjar can show where people click and move on a site. SurveyMonkey helps in making and understanding surveys, and many other tools. These tools help designers understand what users like, what they don’t like, and how they use a website, so they can make it better for everyone.
It was very interesting and informative.🙏🏻
Thank you Johnson
Hey, cool post You can check if there’s a problem with your website with Internet Explorer. Because of this issue, many readers will overlook your excellent writing because IE is still the most popular browser.
Yes, you are right
Isn’t the user’s movement on the page and satisfaction with the design the responsibility of the UI?
Hello Samane,
While the user interface (UI) certainly plays a role in influencing the user’s movement on the page and satisfaction with the design, it is not solely responsible for these aspects. Other factors such as content quality, relevance, and accessibility also contribute significantly to the user’s experience. Additionally, the user’s own preferences, expectations, and prior experiences can influence their interaction with a website or application. While the UI can greatly enhance usability and provide guidance, it is important to consider the broader context and user-centric approach to ensure a satisfactory digital experience.
VUI is mostly used for what parts?
Hello Tony,
VUI, or Voice User Interface, is primarily utilized for enabling voice-activated interactions in various devices and applications. Common uses of VUI include voice-controlled virtual assistants in smartphones, smart speakers, and other smart devices. Additionally, VUI is integrated into automotive systems for hands-free operation, enabling drivers to interact with vehicle controls and infotainment systems while keeping their hands on the wheel. It’s also employed in voice-activated appliances, home automation systems, and interactive voice response (IVR) systems for customer service. Furthermore, VUI is increasingly used in healthcare for voice-activated medical devices and in gaming for immersive, hands-free gameplay experiences, offering users a convenient and accessible way to interact with technology using their voice.
Thank you
Can you explain more about InVision and Miro tools?
Hello Patrick,
InVision and Miro are popular design and collaboration tools. InVision is primarily used for prototyping and UX design, allowing designers to create interactive prototypes and gather feedback. It also offers project management features. On the other hand, Miro is a collaborative online whiteboard platform that facilitates visual collaboration, brainstorming, and ideation. It allows teams to work together in real-time, creating diagrams, mind maps, and other visual assets. Both tools integrate with other software, making it easier to incorporate them into existing workflows. InVision is widely used for design iteration and stakeholder feedback, while Miro is favored for remote collaboration and visualizing ideas. Many design teams use a combination of both tools to streamline their design processes and enhance collaboration.
Thank you